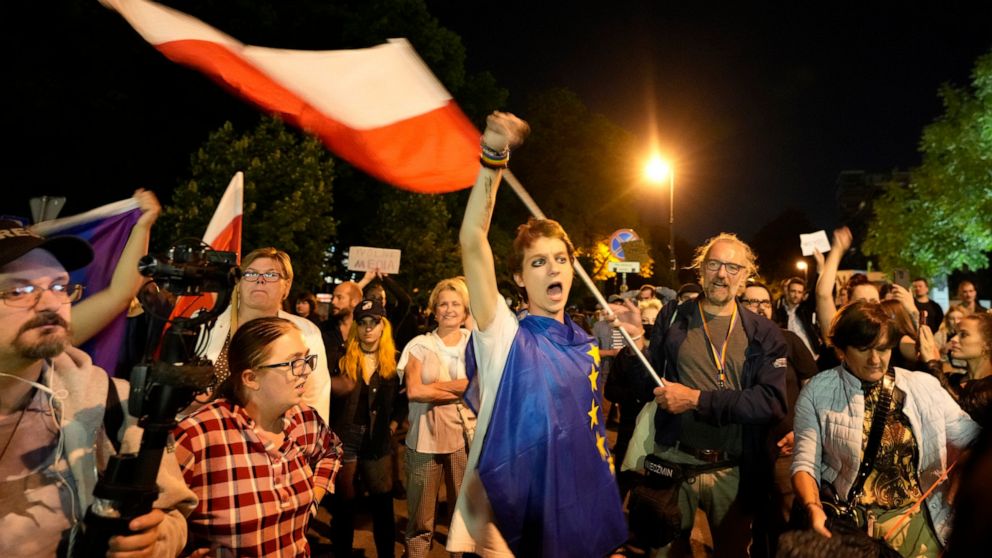Media, Holocaust bills test Poland’s ties with US, Israel
WARSAW, Poland — Poland is looking at a more difficult relationship with two allies, the United States and Israel, after lawmakers passed separate bills — one dealing with foreign ownership of media and the other affecting the property rights of the families of Holocaust survivors — which the Polish government had been warned to drop.
The European Union also slammed the media bill on Thursday as undermining media freedom, adding to pre-existing strains between Warsaw and Brussels from the EU’s perception of democratic backsliding in member nation Poland.
The bills passed the lower house of the Polish parliament on Wednesday, and still require Senate approval and the signature of the president, who supports the right-wing party that has governed the country since 2015.
The two proposals threaten to further isolate Poland, whose geographic position in Central Europe has often left it at the mercy of stronger neighbors, and whose membership in EU and NATO and relationship with the U.S. are considered key guarantees of the country’s future security.
One of the bills that passed would push Discovery Inc., the U.S. owner of Poland’s largest private television network, to sell its large and popular Polish network, TVN. The other would prevent former property owners, including Holocaust survivors and their descendants, from regaining property expropriated by the country’s communist regime.
U.S. Secretary of State Antony Blinken issued a statement late Wednesday about what he called the “troubling legislation,” saying that the NATO alliance to which Poland belongs “is based on mutual commitments to shared democratic values and prosperity.”
“These pieces of legislation run counter to the principles and values for which modern, democratic nations stand,” Blinken said.
Prime Minister Mateusz Morawiecki responded Thursday by suggesting the U.S. officials do not understand the Polish bills and should analyze them more closely.
On the media bill, Morawiecki said: “We do not have any intentions regarding a specific television channel. It is just about tightening the regulations so that there is no situation in which companies from outside the European Union would freely buy media in Poland.”
In anticipation of a parliamentary vote, the bill triggered nationwide protests Tuesday. Among the participants expressing fear that their right to independent information was under attack were older Poles who remember the censorship of the communist era.
By contrast, the law which would affect the former property owners — both Jewish and non-Jewish — got almost no media coverage in Poland. But it sparked a fast and angry response from Israel, with Foreign Minister Yair Lapid saying it “damages both the memory of the Holocaust and the rights of its victims.”
The EU Commission, which polices EU law, said it will follow the media issue very closely while the EU’s top watchdog for democratic values, Vera Jourova, tweeted that the foreign ownership bill sends a negative signal.
“Media pluralism and diversity of opinions are what strong democracies welcome, not fight against,” Jourova wrote. “We need a #MediaFreedomAct in the whole EU to uphold media freedom and support the rule of law.”
European Parliament President David Sassoli also weighed in on the media vote, calling it “very worrying.”
“If the law comes into force, it will seriously threaten independent television in the country. There can be no freedom without a free media,” he said.
The development looked to many like a crucial move in a step-by-step dismantling of the democratic standards that Poland embraced when it threw off communism in 1989.
Hungary had already set the trail for such an illiberal political direction, and the EU has shown little ability so far to do much to ensure adherence to its values either there or in Poland, both previously models of democratic transformation.
After communism ended more than three decades ago, many foreign investors entered Poland’s media market. Poland’s ruling party, led by the country’s de facto leader, Jaroslaw Kaczynski, has long seen this as a problem and sought to “repolonize” the media. The party argues that keeping Polish entities in control of the media is a matter of national security and that such regulations are in line with Western European standards.
However, the party’s critics see the efforts to nationalize media as a pretext for silencing independent voices. The effort is well on its way. Soon after winning power in 2015, Law and Justice transformed tax-funded public media into a party mouthpiece. Last year the state oil company bought a large private media group that owned newspapers, magazines and internet portals, and has since moved to changing the editors.
Some fear the internet could be next after Kaczynski said in July that “the other side” has the advantage there and “we will still have to strive to change this situation.”
On Thursday, TVP Info, the public broadcaster’s all-news station, declared that the parliament had defended “Polish sovereignty” with its media bill.
Independent journalists have a different view. A letter in defense of TVN had gathered the signatures of over 1,000 Polish journalists on Thursday.
———
Raf Casert in Brussels contributed.
![]()